
The Basics of Diamond Quality
According to the Gemological Institute of America (GIA), a diamond’s quality and value are determined by the 4 C's – color, clarity, cut, and carat weight.
The 4 C's provide an objective way to compare and evaluate diamonds. However, numbers alone can’t describe a diamond’s beauty. Visit Wade Jewelers to find out for yourself.

Color attributes of diamonds
Although quality diamonds look colorless, truly colorless diamonds are extremely rare. Diamonds that are used in jewelry are nearly colorless with tints of yellow or brown.
Each diamond is compared to a master set to determine the right color. The GIA color scale ranges from D (colorless) to Z (light yellow or brown). Each letter grade represents a range of color and is a measure of how noticeable a color is.
Some diamonds emit light called fluorescence, when they're exposed to ultra violet radiation. This factor is not considered in color or clarity grades.
However, a description of its strength and color is mentioned on GIA reports as an identifying characteristic.
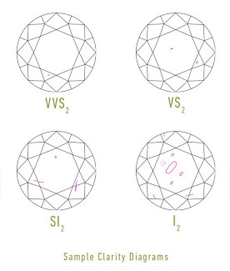
Authentic diamond clarity
The GIA clarity scale consists of 11 clarity grades, ranging from Flawless to I3.
Diamonds form under tremendous heat and pressure; therefore, it’s very difficult to find a diamond that lacks any internal and external characteristics.
These characteristics are a by-product of its formation. They help gemologists distinguish natural diamonds from synthetics and simulants and also help them identify individual stones.
Diamond cut and the effect on quality
The GIA cut scale of diamond ranges from excellent to poor. The beauty of polished diamond lies in its complex relationship with light.
Following are three attributes of a diamond’s cut as related to value:
• Brightness – It refers to the combination of all white light reflecting from the surface and interior of a diamond
• Fire – Describing the appearance of “flares” of color emitted from a diamond
• Scintillation – The pattern of light and dark areas and the sparkle you see when the diamond, the light, or the observer moves
A diamond’s proportions affect its light performance, which consecutively affects its beauty and overall appeal.
Diamonds with fine proportions, symmetry, and polish enhance their interaction with light; therefore, they have more brightness, fire, scintillation, as well as greater value.
GIA evaluates these factors for standard round brilliant diamonds that fall in the D to Z color range.
Gauging diamond size by carat weight
Diamond size is measured in terms of carats. One carat is equivalent to 200 milligrams in weight.
A carat is divided into 100 points – similar to pennies in a dollar.
“Many memories and milestones in my family have been commemorated with pieces from Wade Jewelers.”
– Aaron Cordle
For friendly service, on-site jewelry repair, and custom design, call:
